🚀 Quick Start
Overview
FinqLink is a set of APIs for account-to-account payments/transfers (FinqLink Pay) and account information services (FinqLink Data) through open-banking and other local/custom integrations.
How to test
- Get a set of API test credentials (contact Finqware)
- Use the /test/providers/list endpoint to query for the available/supported providers.
- to visualize the providers list (and more) check our public dashboard.
- Create finq-links using the
/testpath:
- payment links using the
/test/links/createendpoint - consent links for account data using the
/test/consents/createendpoint.
- Send the link to someone in order to authorize the payment or to authorize access to account data.
Sandbox testing
rzb_ro- debtor IBAN:RO03RZBR0000069999999999, creditor IBAN:RO10RZBR0000069999999970, PSU ID:9999999998bt_ro- username:testbt, password:testbt, pin:1234567cec_ro- username:testcecapi, password:testcecapi, IBAN:RO42CECEAG0202RON0007466
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- 🚀 Quick Start
📋 Changelog
Version 2.0 Changelog
This document outlines all changes between FinqLink API v1 and v2, including new features, enhancements, and breaking changes.
Overview
FinqLink v2 is a major release that introduces:
- FinqLink Data (Beta) - Account Information Services (AIS) for accessing bank account data
- Enhanced Pay APIs - Pagination, filtering, and new link statuses
- Custom WebUI Templates - 7 customizable UI themes for payment and consent flows
- Providers API Enhancements - AIS methods support and improved response formats
New: Account Information Services (AIS) - FinqLink Data
The most significant addition in v2 is the complete Account Information Services (AIS) functionality, branded as FinqLink Data. This enables bank account data access alongside existing payment initiation capabilities.
Note: FinqLink Data is currently in Beta. Contact Finqware to enable AIS access for your API client.
New API Endpoints
All AIS endpoints are available on /v2 API paths only (not available in v1):
| Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|
POST /ais/consents/create |
Create a new AIS consent for data access |
POST /ais/consents/get |
Retrieve consent details and current status |
POST /ais/consents/revoke |
Revoke an active consent |
POST /ais/consents/redirect |
Handle SCA callback redirect (direct_sca flow) |
POST /ais/transactions/list |
List transactions with filtering and keyset pagination |
POST /ais/accounts/list |
List accounts with balance information |
POST /ais/balances/list |
List balance history with pagination |
POST /ais/jobs/create |
Trigger an on-demand data refresh job |
POST /ais/jobs/get |
Get data refresh job status |
Consent Lifecycle
AIS consents follow this lifecycle:
created → started → requested → sca_url_retrieved → awaiting_authz → authorized → active
Terminal states: expired, revoked, failed, suspended
Scope Configuration
Control what data is accessible through consent scope:
- Full scope:
["accounts", "balances", "transactions"]- Access to all account data - Limited scope:
["accounts", "balances"]- Faster job completion, no transaction history
AIS Webhooks
Configure webhooks in consent creation to receive real-time updates:
consent_status_update- Triggered when consent status changes (e.g.,awaiting_authz→active)job_status_update- Triggered when data refresh job completes or fails
Enhanced: Links API
Pagination for /links/list
The /links/list endpoint now supports keyset-based pagination for efficient traversal of large result sets.
Request parameters:
{
"pagination": {
"limit": 50,
"after": "eyJpbnNlcnRlZF9hdCI6..."
}
}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
pagination.limit |
integer | Maximum records per page (1-250, default: 50) |
pagination.after |
string | Keyset cursor from previous response for next page |
Response includes:
{
"pagination": {
"count": 50,
"more?": true,
"after": "eyJpbnNlcnRlZF9hdCI6Li4u"
},
"links": [...]
}
New Filter Options
Filter payment links by multiple criteria:
| Filter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
filter.status |
string | Filter by payment status (created, completed, failed, etc.) |
filter.inserted_at_from |
datetime | Links created after this timestamp |
filter.inserted_at_to |
datetime | Links created before this timestamp |
Example:
{
"filter": {
"status": "completed",
"inserted_at_from": "2024-01-01T00:00:00Z"
},
"pagination": {
"limit": 100
}
}
New Payment Link Statuses
Additional statuses for enhanced payment tracking (available for libra_ro, work-in-progress for other providers):
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
funds_received |
Funds confirmed received by creditor bank (via webhook) |
funds_rejected |
Funds rejected by creditor bank (via webhook) |
Enhanced: Providers API
AIS Methods Support
The /providers/list and /providers/get endpoints now support AIS method discovery:
New options:
| Option | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
options.show_ais_methods |
boolean | Include AIS method details in response |
options.ais_methods_filter.account_owner_type |
array | Filter by account owner type (retail, corporate) |
options.ais_methods_filter.interface_type |
string | Filter by interface type |
options.ais_methods_filter.interface_env |
string | Filter by environment (sandbox, stage, prod) |
Example:
{
"options": {
"show_ais_methods": true,
"ais_methods_filter": {
"account_owner_type": ["retail"],
"interface_env": "prod"
}
}
}
Response Format Change: remitter_type
The remitter_type field format has changed between v1 and v2:
| Version | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|
| v1 | String | "retail" or "corporate" |
| v2 | Array | ["retail"], ["corporate"], or ["retail", "corporate"] |
This change enables payment methods to support multiple remitter types simultaneously.
New: WebUI Custom Templates
Customize the payment and consent authorization UI with pre-built templates.
Available Templates
| Template | Description |
|---|---|
default |
Standard/legacy FinqLink layout |
classic |
Traditional banking interface |
compact |
Minimal, space-efficient layout |
cards |
Card-based provider selection |
glass |
Glassmorphism design with blur effects |
sheet |
Bottom sheet mobile-first design |
Usage
Specify the template in /links/create or /ais/consents/create:
{
"options": {
"ux_template": "glass"
}
}
Note: The
ux_templateoption overrides the default template configured for your API client.
Breaking Changes
1. remitter_type Response Format
Affected endpoints: /providers/list, /providers/get
The remitter_type field in payment method responses has changed from a string to an array:
v1 Response:
{
"payment_methods": [{
"remitter_type": "retail"
}]
}
v2 Response:
{
"payment_methods": [{
"remitter_type": ["retail"]
}]
}
Migration: Update your code to handle remitter_type as an array.
2. AIS Endpoints Availability
AIS endpoints (/ais/*) are only available on /v2 paths. Requests to /v1/ais/* will return a 404 error.
3. Pagination Response Structure
The /links/list endpoint now returns pagination metadata in a structured format:
v1 Response:
{
"links": [...]
}
v2 Response:
{
"pagination": {
"count": 50,
"more?": true,
"after": "cursor_token"
},
"links": [...]
}
Migration: Update your code to extract links from the links array and handle pagination metadata.
Migration Guide
Upgrading from v1 to v2
- Update API path: Change from
/v1/to/v2/ - Handle array
remitter_type: Update providers response parsing to treatremitter_typeas an array - Optional: If using
/links/list, handle the new pagination response structure - Optional - Enable AIS: Contact Finqware to enable FinqLink Data access for your API client
- Optional - Customize UI: Explore the new
ux_templateoptions for branded payment experiences
API Version Support
| Version | Status | End of Life |
|---|---|---|
| v1 | Supported | TBD |
| v2 | Current | - |
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- 📋 Changelog
Security
The Link API is secured by OAuth2 (mandatory for production access) and mTLS (optional).
Mutual TLS (mTLS) and OAuth2 Client Credentials are two distinct security mechanisms that can complement each other to provide robust authentication and secure communication in API integrations.
Note: For testing purposes we also support an internal authentication method that requires
client_id/client_secretwith each API call. The code examples in this document use this particular method.
How mTLS and OAuth2 Client Credentials Complement Each Other
When used together, mTLS and OAuth2 Client Credentials Grant provide a powerful combination of strong client authentication and fine-grained authorization. Here's how they complement each other:
Dual Authentication and Authorization
- mTLS provides a strong, cryptographic client authentication mechanism, ensuring that only authorized clients (those with valid client certificates) can establish a connection.
- OAuth2 Client Credentials provides a token-based mechanism for authorizing the client's access to specific APIs or resources. The access token contains information about the client's permissions and access scope.
Layered Security
By using both mTLS and OAuth2, you establish multiple layers of security. Even if an access token is somehow obtained by an attacker, mTLS ensures that only clients with a valid certificate can connect. Conversely, even if a client possesses a valid certificate, it still needs a valid access token to access protected resources.
Preventing Token Theft and Replay Attacks
With mTLS, the secure communication channel prevents token theft during transmission. Even if a token were somehow intercepted, it would be useless without the client's certificate to establish the connection.
Enhanced Security for Sensitive Applications
For highly sensitive applications, combining mTLS with OAuth2 Client Credentials ensures that only authenticated clients (validated by their certificates) and authorized clients (validated by their tokens) can access resources. This is particularly important in zero-trust environments or for internal microservices communication.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Some industries require strong client authentication and end-to-end encryption. Combining mTLS with OAuth2 can help meet these regulatory requirements by ensuring secure communication and controlled access.
Summary
By combining mTLS with OAuth2 Client Credentials Grant, you gain the benefits of both strong client authentication and fine-grained access control, enhancing the overall security posture of your application.
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Security
mTLS
mTLS is a mechanism for ensuring that both the client and server authenticate each other over a TLS connection. It is an extension of standard TLS (which typically only authenticates the server to the client).
How mTLS Works
- Client Authentication: In addition to the server presenting its certificate, the client also presents its own certificate to the server.
- Certificate Verification: Both parties verify the certificates they receive. This ensures that both the client and server are who they claim to be, providing bidirectional authentication.
- Secure Communication: Once both parties are authenticated, a secure encrypted communication channel is established.
Benefits of mTLS
- Strong, cryptographic client authentication.
- Prevents unauthorized clients from connecting to the server.
- Ensures data integrity and confidentiality during transmission.
Setup
Setting up mTLS requires two steps. Please contact us for:
- Enabling your API Client for mTLS
- Sharing your certificates in order to be added to our PKI infrastructure
Certificate Requirements
Certificates must use either RSA or ECDSA ciphers.
For client (leaf) certificates:
- The
BasicConstraintsextension must not containCA=true - The
ExtendedKeyUsageextension must containclientAuth - The
ExtendedKeyUsageextension must not contain thecodeSigning,timeStamping, orOCSPSigningfields - The certificate must not be expired
- The client certificate cannot be a self-signed certificate
- The
For root and intermediate certificates:
- The
BasicConstraintsextension must containCA=true - The
KeyUsageextension must be set tokeyCertSign - The
ExtendedKeyUsageextension should contain theclientAuthfield - The certificate must not be expired
- The
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- mTLS
OAuth2
OAuth2 Client Credentials Grant is a method for obtaining access tokens that can be used to authenticate requests to an API. It is typically used when a client (such as a service or application) needs to access resources or APIs on behalf of itself, not on behalf of a user.
How OAuth2 Client Credentials Grant Works
- The client (service or application) authenticates with the authorization server using its client ID and secret.
- If the credentials are valid, the authorization server issues an access token.
- The client uses this access token to authenticate its requests to the resource server (API).
Benefits of OAuth2 Client Credentials
- Provides a mechanism for API clients to obtain access tokens for authenticating requests.
- Supports fine-grained authorization and scopes to control access to resources.
- Enables centralized management of client credentials and access policies.
Private Key JWT
Private Key JWT is a method of client authentication where the client creates and signs a JWT using its own private key. This method is described in a combination of RFC 7521 (Assertion Framework) and RFC 7523 (JWT Profile for Client Authentication), and referenced by OpenID Connect and FAPI 2.0 Security Profile.
Although we support the Client Secret (RFC 6749) authentication, we recommend Private Key JWT as it does not involve a process of sharing secrets.
Setup
Setting up OAuth2 requires a few steps. Please contact us for:
Enabling your API Client for OAuth2
Sharing the public key which we'll use to verify the signed requests to our Authorization server. Example script for generating the public/private key pair:
#!/bin/bash # Generate private key in PEM format openssl genpkey -algorithm RSA -out private.key.pem -pkeyopt rsa_keygen_bits:2048 # Generate public key in PEM format (intermediate step) openssl rsa -pubout -in private.key.pem -out public.key.pem # Convert private key to JWK (JSON Web Key) format private_jwk=$(openssl rsa -in private.key.pem -noout -text | \ awk ' /modulus:/{p=1;next}/publicExponent:/{p=0}p' | \ tr -d ' \n:' | \ xxd -r -p | base64 -w 0 | \ tr '+/' '-_' | tr -d '=') private_exp=$(openssl rsa -in private.key.pem -noout -text | \ awk '/privateExponent:/{p=1;next}/prime1:/{p=0}p' | \ tr -d ' \n:' | \ xxd -r -p | base64 -w 0 | \ tr '+/' '-_' | tr -d '=') # Convert public key to JWK format modulus=$(openssl rsa -pubin -in public.key.pem -modulus -noout | \ cut -d'=' -f2 | \ xxd -r -p | base64 -w 0 | \ tr '+/' '-_' | tr -d '=') # Generate key ID (kid) kid=$(openssl rand -hex 32) # Create public key JWK echo "{ \"kty\": \"RSA\", \"kid\": \"$kid\", \"n\": \"$modulus\", \"e\": \"AQAB\", \"alg\": \"RS256\", \"use\": \"sig\" }" > public.key.json # Create private key JWK echo "{ \"kty\": \"RSA\", \"kid\": \"$kid\", \"n\": \"$modulus\", \"e\": \"AQAB\", \"d\": \"$private_exp\", \"alg\": \"RS256\", \"use\": \"sig\" }" > private.key.json echo "Keys generated successfully!" echo "Files created:" echo "- private.key.pem (Private key in PEM format)" echo "- private.key.json (Private key in JWK format)" echo "- public.key.json (Public key in JWK format)" # Display the generated kid for reference echo -e "\nKey ID (kid) for reference:" echo "$kid"
Getting an Access Token
Making requests to the Link API in production requires a valid Bearer access token, sent via the standard Authorization header. The process below describes the way to acquire an access token. Example script:
#!/bin/bash
# Your API client id
CLIENT_ID="0o....17"
# The /token endpoint
AUD="https://finqware.okta.com/oauth2/ausfqbxutkZBUKUgQ417/v1/token"
# The key id (kid) of your key
KID="t4cs...j3s"
# Your private key in PEM format
PRIVATE_KEY_PATH="./private.key.pem"
# Generate timestamps
iat=$(date +%s)
exp=$((iat + 3600))
# Create JWT header (Base64URL-encoded)
HEADER=$(echo -n '{"alg":"RS256","typ":"JWT","kid":"'"$KID"'"}' | openssl base64 -e -A | tr '+/' '-_' | tr -d '=')
# Create JWT payload (Base64URL-encoded)
PAYLOAD=$(echo -n '{"aud":"'"$AUD"'","iss":"'"$CLIENT_ID"'","sub":"'"$CLIENT_ID"'","iat":'"$iat"',"exp":'"$exp"',"jti":"'"$(uuidgen)"'"}' | openssl base64 -e -A | tr '+/' '-_' | tr -d '=')
# Combine header and payload
DATA="$HEADER.$PAYLOAD"
# Sign the JWT using RS256
SIGNATURE=$(echo -n "$DATA" | openssl dgst -sha256 -binary -sign "$PRIVATE_KEY_PATH" | openssl base64 -e -A | tr '+/' '-_' | tr -d '=')
# Final JWT (signed client_assertion)
JWT="$DATA.$SIGNATURE"
echo "Generated JWT (signed client_assertion):"
echo "$JWT"
echo -e "\n"
# Create the curl command with the generated JWT
echo -e "\nCurl command:"
echo "curl --location --request POST '$AUD' \\
--header 'Accept: application/json' \\
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \\
--data-urlencode 'client_id=$CLIENT_ID' \\
--data-urlencode 'grant_type=client_credentials' \\
--data-urlencode 'scope=pay_by_link' \\
--data-urlencode 'client_assertion_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:client-assertion-type:jwt-bearer' \\
--data-urlencode 'client_assertion=$JWT'"
echo -e "\n"
echo -e "\nRetrieving the authz Bearer token..."
curl --location --request POST "$AUD" \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--data-urlencode "client_id=$CLIENT_ID" \
--data-urlencode 'grant_type=client_credentials' \
--data-urlencode 'scope=pay_by_link' \
--data-urlencode 'client_assertion_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:client-assertion-type:jwt-bearer' \
--data-urlencode "client_assertion=$JWT"
Your backend is responsible to implement a mechanism for keeping an up-to-date access-token available at all times. There are mature libraries for implementing this process, available in all mainstream programming languages (e.g., Java, NodeJS).
Step 1: Build the Client Assertion JWT
Build a token with a payload such as below and sign it with your private key. The signed token is called a client_assertion in OAuth2 terms.
The example below assumes your client_id is xyz123abc and key id (kid): a1b2c3:
JSON Header (must specify your key id):
{
"alg": "RS256",
"typ": "JWT",
"kid": "a1b2c3"
}
JSON Payload:
{
"aud": "https://finqware.okta.com/oauth2/ausfqbxutkZBUKUgQ417/v1/token",
"iss": "xyz123abc",
"sub": "xyz123abc",
"iat": 1741161292,
"exp": 1741164892,
"jti": "9CF1E...479C"
}
Step 2: Request Access Token
Use the client_assertion computed above to make a call to our /token endpoint in order to get an access-token:
curl --location --request POST 'https://finqware.okta.com/oauth2/ausfqbxutkZBUKUgQ417/v1/token' \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--data-urlencode 'client_id=xyz123abc' \
--data-urlencode 'grant_type=client_credentials' \
--data-urlencode 'scope=pay_by_link' \
--data-urlencode 'client_assertion_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:client-assertion-type:jwt-bearer' \
--data-urlencode 'client_assertion=eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsIn....le3qGb5mp-yUmPqUwoyZaA9g'
Step 3: Use the Access Token
Use the received access-token for making calls to the Link API until its expiration (each access-token is valid for a limited time).
Include the token in the Authorization header:
Authorization: Bearer your_access_token
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- OAuth2
Webhook signing and callbacks
Webhook requests (payment status, consent status, job status) are signed so you can verify they come from FinqLink. You can also restrict incoming requests to our callback IPs.
Headers
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
x-signature |
JWS compact string (header.payload.signature, Base64URL). The signed payload is the raw JSON body of the request. |
x-signature-kid |
Key ID of the key used to sign; use it to select the key from the JWKS for verification. |
How to verify
- Fetch the public keys:
GET {base_url}/.well-known/jwks.json(use your environment base URL). Response shape:{"keys": [ { "kty", "kid", "alg", "use", "n", "e" }, ... ]}. - From the webhook request: read the
x-signature-kidandx-signatureheaders and the raw request body (UTF-8 JSON). - Find the key in
keyswith matchingkid. Verify the JWS inx-signature: the JWS payload must equal the raw body, and the signature must verify with that key (RS256 or ES256 per key'salg). Reject ifkidis unknown, signature is invalid, or payload does not match body.
Key rotation policy
Signing keys are rotated automatically at a regular interval. The current key is used to sign new webhook requests and remains in use for approximately 90 days until the next rotation. When a new key is introduced, the previous key stays published in JWKS so you can continue to verify webhooks that were signed with it (for example, requests sent just before or during the rotation). The previous key remains available in JWKS for approximately 90 days after it is replaced. After that, it is removed from JWKS and webhooks signed with it can no longer be verified—treat any webhook whose x-signature-kid is not present in JWKS as invalid.
JWKS endpoint and key versions
GET /.well-known/jwks.json returns the public keys you need to verify webhook signatures. The endpoint always lists exactly two keys: the current key (used for new webhooks) and the previous key (used for webhooks sent before the latest rotation). Keys are ordered newest first. Use x-signature-kid from each webhook to pick the right key for verification. If you receive a webhook with a kid that is not in the JWKS response, do not trust it (it may be a replay or from an outdated integration).
JavaScript verification example (Express + jose)
This example uses Express with a raw body parser and the jose library to verify the webhook signature against the remote JWKS. The signed payload must match the raw request body byte-for-byte, so do not use express.json() for the webhook route—use express.raw().
import express from "express";
import { compactVerify, createRemoteJWKSet } from "jose";
const app = express();
// Capture raw body as Buffer
app.use(express.raw({ type: "application/json" }));
const BASE_URL = process.env.FINQWARE_BASE_URL; // e.g. https://sandbox-pay.finqware.com
const JWKS = createRemoteJWKSet(new URL(`${BASE_URL}/.well-known/jwks.json`));
app.post("/webhook", async (req, res) => {
try {
const sig = req.header("x-signature");
const kidHeader = req.header("x-signature-kid");
if (!sig || !kidHeader) return res.sendStatus(401);
// Verify signature (jose picks key by kid from the JWS header)
const { payload, protectedHeader } = await compactVerify(sig, JWKS);
// Optional defense-in-depth: compare kid values
if (protectedHeader?.kid && protectedHeader.kid !== kidHeader) {
return res.sendStatus(401);
}
// Payload must match raw body exactly
const rawBody = req.body; // Buffer from express.raw
if (Buffer.compare(Buffer.from(payload), rawBody) !== 0) {
return res.sendStatus(401);
}
// At this point: signature valid + body matches
// Now you can JSON.parse(rawBody.toString("utf8")) safely
res.sendStatus(200);
} catch (e) {
res.sendStatus(401);
}
});
app.listen(3000);
Callbacks from fixed IPs
You can restrict your webhook endpoint to accept requests only from FinqLink's outbound IPs:
| Environment | Outbound IP |
|---|---|
| Test | 34.89.170.122 |
| Production | 34.159.239.125 |
Use firewall or load-balancer rules to allow only these source IPs for the path that receives webhooks.
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Webhook signing and callbacks
Pay APIs
Payment initiation and provider discovery endpoints.
Overview
FinqLink Pay is a set of APIs for account-to-account payments/transfers through open-banking and other local/custom integrations (eg: RoPay in Romania).
The platform enables API clients to create payment links that allow end-users to complete payments through their banking providers using Strong Customer Authentication (SCA).
Pay-by-link is a method that breaks the payment process in two distinct phases:
- the creation of a payment request, operated by the creditor (receiver of funds)
- the acceptance & authorization of the payment, operated by the debtor (the source of funds)
The payment request encapsulates metadata such as: amount, currency, the list of goods to be acquired etc. Once its created, the payment request is wrapped into a transportable object - aka the link- such as a URL or a QR code. The link is sent to a debtor who will only check/approve & authorize the payment.
Payment providers
A payment-provider is a partner institution that operates payment services. FinqLink integrates with these providers over APIs such as open-banking payment initiation APIs.
Each provider has a unique code. Eg: rzb_ro, cec_ro etc.
A provider may have one or multiple payment-methods offering different capabilities (domestic-only transfers, corporate-only transfers etc)
we provide an API and a dashboard for quering and visualising all the details regarding providers & methods.
Payment Flow Types
The API supports multiple payment flow types:
- link: Default web-based payment experience via FinqLink WebUI
- wrapped_sca: SCA URLs wrapped in a transportable link operated via FinqLink WebUI
- direct_sca: Mobile app-to-app experience with direct bank redirect (requires a custom eIDAS certificates setup)
- redirect_sca: Mobile app-to-app experience with redirect via FinqLink WebUI
The FinqLink Pay WebUI
The WebUI is a web application that facilitates the payment process by providing a user interface for the end-user to complete the payment. It comes with a payment-method selection component, payment details and real-time status updates.
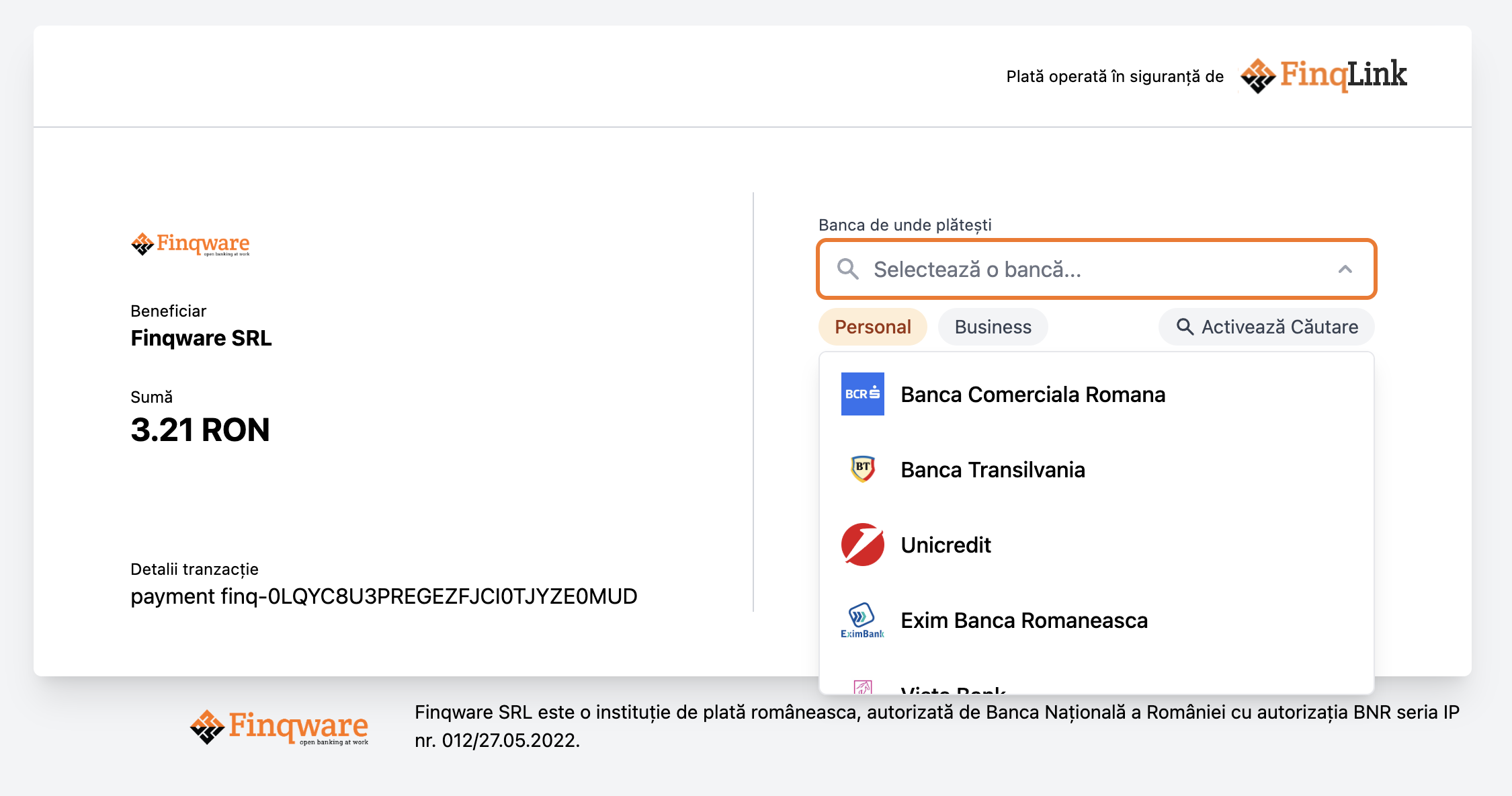
Webhooks
The API supports webhook notifications for payment status updates. Configure webhook URLs when creating payment links. Webhook payloads include:
type: Event type (e.g., "link_status_update")link_id: The payment link UUIDweb_id: The public web identifierstatus: New payment status
Decimal Values
Monetary amounts are represented as strings to maintain precision (e.g., "100.50").
- No leading zeros allowed (except for values less than 1, e.g., "0.50")
- No comma separators allowed
- Decimal point is optional for whole amounts
On this page
- Pay APIs
Data APIs
Account Information Services (AIS) endpoints for accessing banking data.
Note: This API is in public beta and may be slightly changed based on your feedback.
Webhooks are supported for:
- Consent status updates: Notified when consent status changes (e.g.,
started→active) - Job status updates: Notified when data refresh jobs complete or change status
Banking data retrieval endpoints for accounts, balances, and transactions.
Pagination
The transactions and balances list endpoints use keyset-based pagination.
Use the keyset value from the last record as the after parameter
in your next request to fetch the next page.
Filtering
All data endpoints support filtering by various criteria:
- Accounts: currency, account type
- Balances: currency, type, account ID
- Transactions: amount range, date range, credit/debit indicator, status
Balance Types
Check the balance types documentation for more details.
On this page
- Data APIs